4 December, 2019
Is coconut oil as beneficial as they say?

In nutrition it seems that everything is about new foods with great health effects. It seems that the foods we’ve had for our whole lives aren’t good enough, we grew tired of them and we must always incorporate some new ones. Today’s new food is coconut, specifically coconut oil. But is it coconut oil or coconut fat? What are the properties of coconut oil? Do MCT oil and coconut fat have the same properties? Now, Let’s see…
COCONUT OIL OR COCONUT FAT?
Let’s start by its name. What is “coconut oil“? Oils are those lipids that are liquid at room temperature, whereas if they are solid they are called fats, because their solid state is due to the fatty acids that compose them. The higher the saturated fat content, the more solid it will be at room temperature. Since 82%1 of the content of “coconut oil” is saturated fat, at room temperature this product is in solid state. Which means it should really be called coconut fat. So why is it called oil? I wouldn’t know what to answer, maybe it’s just generalized nomenclature, just like everyone calls “milk “vegetable drinks that come from soy, almonds, etc.
“Considering that 82%1 of the content of “coconut oil” is saturated fat, at room temperature this product is in solid state. So it should really be called coconut fat.
IF IT IS SATURATED FAT, WHY ARE ALL THESE HEALTH BENEFITS ATTRIBUTED TO COCONUT OIL?
(Here comes a little more biochemistry, hopefully I won’t tire you out)
The lipids – commonly called fats – are formed by a molecule of glycerol and one, two or three fatty acids attached to it. These fatty acids can be of short, medium or long chain. They can also be saturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated, depending on the number of double bonds they contain. The most common fats in food are the long-chain triglycerides , but with the latest fashion of ketogenic diets, much is being said about the medium-chain triglycerides (MCT).
o MCT oil and the ketogenic diet
100% MCT oil is the only one that could show some health benefits.2 Since MCT oil comes from coconut oil, the benefits of MCT oil tend to be equated to the benefits of coconut oil. But it’s not so. MCT oil and coconut fat are not equivalent.3
Admittedly, MCT oil is extracted from coconut, but I insist it is 100% MCT. To obtain this, the other triglycerides contained in coconuts- which made up around 50% of them – have been eliminated. Supposedly, within the so-called MCT, the shorter the chain, the greater the effect than is sought with the ketogenic diet. That is to say: increase in satiety, easier digestion and absorption of these fats as well as increased liver production of ketone bodies to favor weight loss. Coconut fat contains 42% of lauric acid, which is the longest chain within the MCTs. However, within the human body it behaves as a long-chain triglyceride, not as a medium one. Therefore, this reinforces the concept that MCT oil and “coconut oil” are not the same thing and do not share the same properties.
“Although MCT oil is obtained from coconut, MCT oil and coconut oil are NOT the same thing and do NOT share the same properties”
SHOULD WE INTRODUCE COCONUT OIL IN OUR DIET?
The answer depends on which fat or oil is normally used for cooking. If the answer is virgin olive oil, I think changing to fat or coconut oil for cooking isn’t such a good idea. Whereas if butter, lards and other fats are prevalent, there may be some health benefits in swapping for coconut oil4. In any case, this is not the only factor to consider. Let’s not forget that the combination of food variety and lifestyle is what really makes a difference. The following graphs explain why I think so5 :
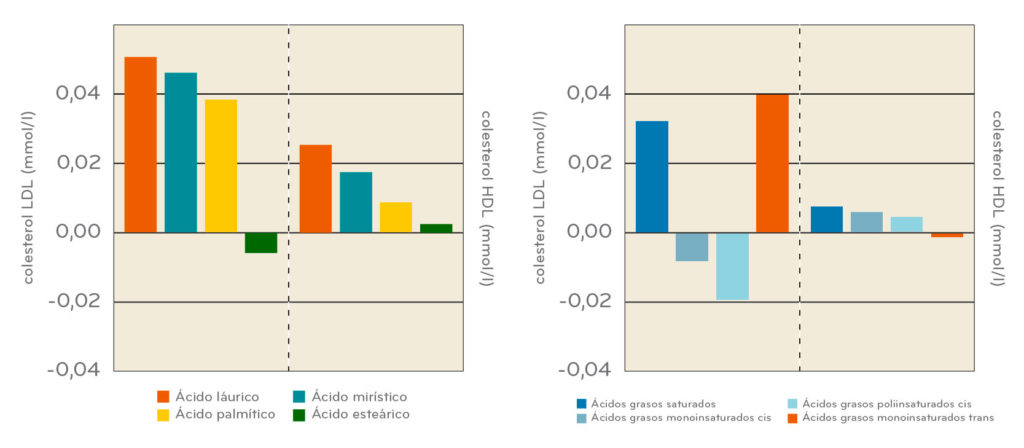
PICTURE 1. Effect of saturated fatty acids on LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol. PICTURE 2. Effect of dietary fatty acids on serum concentrations of HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in a meta-analysis of 60 controlled studies.
I shall translate the data: we said before that coconut fat is made of 42% lauric acid, a saturated fat. As the first graph shows, it favors the increase of c-LDL (bad cholesterol) in blood, and increases c-HDL (good cholesterol) to a lesser extent than the bad one. It also contains AGMI in the form of oleic acid, but it’s only 6%. Compared to olive oil – which contains 14% AGS and 70% AGMI, as shown in the second graph – AGMI not only increases the good cholesterol, but it also reduces the bad one.
“If you usually use virgin olive oil for cooking and dressing, I don’t think it’s a good idea to switch to coconut fat. If you cook with butter, lard or other fats, swapping may bring some benefits”
COCONUT OIL IN COOKING
When oils or fats reach their smoking point, they gaseous vapours are formed and the oil or fat loses its properties. Coconut fat or coconut oil‘s smoking point is 170-232ºC (depending on the data source)6.7 . This means that it withstands high temperatures well and does not burn easily. Olive oil’s smoking point varies between 160ºC and 242ºC, depending on its refining. This comparison suggests that cooking with coconut oil brings great benefits. What really matters is to always make sure we’re cooking with oils that best withstand temperatures.
IS COCONUT OIL A “SUPER FOOD”?
One of the most widely used statements to support the properties of coconut oil is that the populations that have been consuming it for centuries are overall healthy. However, this must always be considered in context. After all, we’re talking about lifestyles 8 so we can’t focus on just one food and attribute to it all the properties and benefits. This is something we tend to do when talking about superfoods. If this were the case, we could say that also olive oil is a “superfood”. Admittedly it is a great food, though its main benefits arise in the framework of the Mediterranean diet. To sum up, if virgin olive oil is the main source of fat in your diet, do not swap for the “famous” coconut oil.
1. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/343868/nutrients
2. St-Onge MP, Mayrsohn B, O’Keeffe M, Kissileff HR, Choudhury AR, Laferrère B. Impact of medium and long chain triglycerides consumption on appetite and food intake in overweight men. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct; 68(10):1134-40.
3. Kinsella R, Maher T, Clegg ME. Coconut oil has less satiating properties than medium chain triglyceride oil. Physiol Behav. 2017 Oct 1;179:422-426.
4. Schwingshackl L, Bogensberger B, Benčič A, Knüppel S, Boeing H, Hoffmann G. Effects of oils and solid fats on blood lipids: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Lipid Res. 2018 Sep; 59(9):1771-1782.
5. Guía de alimentación cardiosaludable en atención primaria. 2ª Ed. España: Innuo SL; 2007.
6. Boateng L, Ansong R, Owusu WB, Steiner-Asiedu M. Coconut oil and palm oil’s role in nutrition, health and national development: A review. Ghana Med J. 2016 Sep; 50(3):189-196.
7. https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Punto_de_humeo
8. Eyres L, Eyres MF, Chisholm A, Brown RC. Coconut oil consumption and cardiovascular risk factors in humans. Nutr Rev. 2016 Apr; 74(4):267-80.






