3 October, 2019
Treatment of acute glaucoma
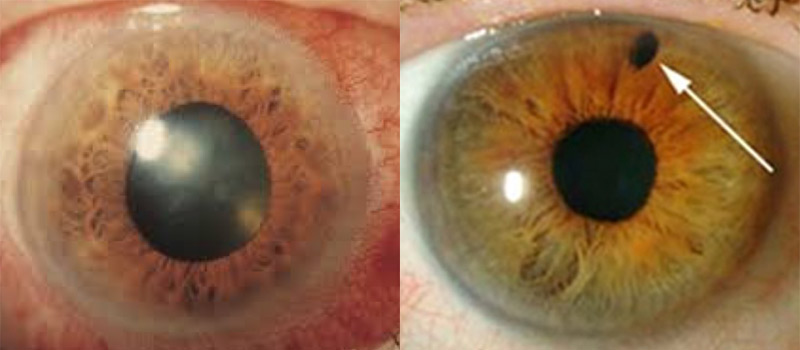
The manifestations of acute glaucoma are completely different to chronic glaucoma. The main difference is the presence of numerous acute glaucoma symptoms: very severe eye pain, loss of vision, photophobia and, occasionally, general malaise accompanied by nausea and reflex vomiting. The main cause of acute glaucoma is sudden and severe blockage of the aqueous humour or intraocular fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye.
TREATMENT OF ACUTE GLAUCOMA
Medication
Acute glaucoma is treated by general medication, such as hyperosmolar agents. These drugs cause the eye tissue to “dehydrate”, forcing out fluid from inside. They are usually administered intravenously. However, there are also diuretics which do the same job that are administered orally.
Eye drops
It is also possible to use eye drops to reduce intraocular pressure, such as those mentioned in previous posts. Eye drops that cause the pupil to close can also be used to mechanically move the iris that is “blocking” the drainage angle of the anterior part of the eye.
YAG laser peripheral iridotomy
However, the primary treatment to be implemented is called YAG laser peripheral iridotomy (PI). During peripheral iridotomy, a small hole is made in the iris to allow the fluid in the eye to circulate freely. The hole helps drain this fluid and thus reduce intraocular pressure. This treatment for acute glaucoma provides instant relief for the patient, as the accumulated fluid is immediately removed.
SYMPTOMS OF ACUTE GLAUCOMA AND POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCES
Acute glaucoma is a very serious condition that causes numerous complications for the patient. As we have already mentioned, the symptoms of acute glaucoma include significant eye pain, general malaise, nausea and reflex vomiting. If it is not treated immediately, it may lead to irreversible loss of visual acuity. And even if treated early, the consequences may still be serious, such as loss of visual field, non-reactive mydriasis, lens opacity, etc.
WHO CAN SUFFER FROM ACUTE GLAUCOMA?
It is important that patients with hypermetropia, who have eyes with short axial length or a family history of acute glaucoma go to their ophthalmologist. These patients should be checked whether they have an eye at risk of acute glaucoma and are likely to require prophylactic peripheral iridotomy. This is particularly important for those patients who already exhibit some type of symptom, such as eye pain, headache or coloured vision halos when looking at light, especially in low light conditions.
INTRAOCULAR LENS TO PREVENT ACUTE GLAUCOMA
After an episode of acute glaucoma, or in predisposed eyes that already have a significant increase in intraocular pressure, it is recommended that phacoemulsification be performed. Phacoemulsification is a procedure to remove cataracts or the lens (if this has not yet become opaque, causing a cataract) and the placement of an intraocular lens. The objective is to extract a bulky lens from the inside of these small eyes and create a space for the intraocular fluid to freely circulate. The intraocular lens that is inserted inside the eye is flattened and therefore occupies much less space than the lens (physiological lens) of the eye.
“Acute glaucoma is a very serious condition that can result in irreversible loss of visual acuity and requires treatment with YAG laser peripheral iridotomy. Cataract surgery is often recommended in such eyes and eyes which are predisposed to this condition”
Dra. Elena Milla






